# Turtlesim & python
In the previous sections we controlled the turtle mainly by terminal. For most of the case this isn't that interesting. That is why we will be controlling the turtle with a own written python script.
Before creating the python script make sure you're in the correct directory!
WHY?
If you save the files in the wrong directories all will be lost if you exit the container environment. 😮 Noooo!
In the Dockerfile is described that the directory /root/home/catkin_ws is saved. (for the experts: connected to a Docker volume)
cd ~/home/catkin_ws/src/turtlebot3_simulations/turtlebot3_simulations mkdir scripts cd scriptsCopied!
2
3
IMPORTANT
Make sure that roscore and turtlesim_node are still running.
Stop all other terminal execution by CTRL+C
The following things will be handled in this section
- Subscribe to a rostopic
- Move the turtle linear
# Subscribe to a rostopic
The objective of this script is to read the position (Pose) of the turtle.
We will have to subscribe to the /turtle1/Pose topic
WARNING
Work in the following directory!
cd ~/home/catkin_ws/src/turtlebot3_simulations/turtlebot3_simulations/scriptsCopied!
Create a Python script turtlesubscribe.pyand make executable (chmod +x turtlesubscribe.py).
touch turtlesubscribe.pyCopied!
Be sure to be in the correct directory where the program is located. Make Executable
chmod +x turtlesubscribe.pyCopied!
WARNING
If chmod +x is not execute onto the python script it won't run!
If you execute the command ls in the terminal you will see
that the name turtlesubscribe.pyshould be green.
That indicates that it is executable.
lsCopied!
Add the code below to the python script. Open it with nano editor
nano turtlesubscribe.pyCopied!
TIP
Paste it with CTRL + SHIFT + V in nano editor
With CTRL + S you can save the file and with CTRL + X you can close the file.
#!/usr/bin/env python # Set linear and angular values of Turtlesim's speed and turning. import rospy # Needed to create a ROS node # Message that moves base from turtlesim.msg import Pose class ReadTurtlesim: def __init__(self): # ControlTurtlesim is the name of the node sent to the master rospy.init_node('TurtleSubcribe', anonymous=False) # Message to screen rospy.loginfo(" Press CTRL+c to stop TurtleBot") # Keys CNTL + c will stop script rospy.on_shutdown(self.shutdown) # Publisher will send Twist message on topic # /turtle1/cmd_vel self.pose_subscriber = rospy.Subscriber('/turtle1/pose', Pose, self.callbackPose) rospy.spin() def callbackPose(self,msg): print("test") print(msg) def shutdown(self): # You can stop turtlebot by publishing an empty Twist message rospy.loginfo("Stopping Turtlesim") # Give TurtleBot time to stop rospy.sleep(1) if __name__== "__main__": try: ReadTurtlesim() except: rospy.loginfo("End of the trip for Turtlesim")Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
Get file from Github (opens new window)
# Move the turtle linear
The objective is here to move the turtle with the use of the rostopic cmd_vel.
We will have to publish the rostopic.
WARNING
Work in the following directory!
~/home/catkin_ws/src/turtlebot3_simulations/turtlebot3_simulations/scriptsCopied!
Create a Python script turtlemove.pyand make executable (chmod +x turtlemove.py).
touch turtlemove.pyCopied!
Be sure to be in the correct directory where the program is located. Make Executable
chmod +x turtlemove.pyCopied!
WARNING
If chmod +x is not execute onto the python script it won't run!
If you execute the command ls in the terminal
you will see that the name turtlemove.pyshould be green.
That indicates that it is executable.
lsCopied!
Add the code below to the python script. Open it with nano editor
nano turtlemove.pyCopied!
TIP
Paste it with CTRL + SHIFT + V in nano editor
With CTRL + S you can save the file and with CTRL + X you can close the file.
#!/usr/bin/env python # Set linear and angular values of Turtlesim's speed and turning. import rospy # Needed to create a ROS node from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist # Message that moves base class ControlTurtlesim: def __init__(self): # ControlTurtlesim is the name of the node sent to the master rospy.init_node('ControlTurtlesim', anonymous=False) # Message to screen rospy.loginfo(" Press CTRL+c to stop TurtleBot") # Keys CNTL + c will stop script rospy.on_shutdown(self.shutdown) # Publisher will send Twist message on topic # /turtle1/cmd_vel self.cmd_vel = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=10) # Turtlesim will receive the message 10 times per second. rate = rospy.Rate(10); # 10 Hz is fine as long as the processing does not exceed # 1/10 second. rospy.loginfo(" Set rate 10Hz") # Twist is geometry_msgs for linear and angular velocity move_cmd = Twist() # Linear speed in x in meters/second is + (forward) or # - (backwards) move_cmd.linear.x = 0.3 # Modify this value to change speed # Turn at 0 radians/s move_cmd.angular.z = 0 # Modify this value to cause rotation rad/s # Loop and TurtleBot will move until you type CNTL+c while not rospy.is_shutdown(): # publish Twist values to the Turtlesim node /cmd_vel self.cmd_vel.publish(move_cmd) # wait for 0.1 seconds (10 HZ) and publish again rate.sleep() def shutdown(self): # You can stop turtlebot by publishing an empty Twist message rospy.loginfo("Stopping Turtlesim") self.cmd_vel.publish(Twist()) # Give TurtleBot time to stop rospy.sleep(1) if __name__== "__main__": try: ControlTurtlesim() except: rospy.loginfo("End of the trip for Turtlesim")Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Get file from Github (opens new window)
python turtlemove.pyCopied!
You will see that the turtle moves in forward direction.
To stop the script press CTRL + C in the terminal
TIP
The position of the turtle can be reseted by the following command:
rosservice call /resetCopied!
# Exercise 1
Try to move the turtlebot backwards with a script
TIP
- forward movement: positive
- backward movement : negative
Solution Exercise 1
Change line 30 in the python script to the following
move_cmd.linear.x = -0.3Copied!
# Exercise 2
Try to move the turtlebot forward in a circle with a script
TIP
- linear: forward/backward
- angular: turning
Solution Exercise 2
Change line 30 in the python script to the following
move_cmd.linear.x = 1.0 move_cmd.angular.z = 0.8Copied!
2
# Moving to goal
The objective is here to move the turtle to a specific goal. This by using the combination of the cmd_vel and pose topic
By reading the current pose of the turtle (subscribing to the pose topic ) and comparing by the requested goal the cmd_vel can be published.
WARNING
Work in the following directory!
~/home/catkin_ws/src/turtlebot3_simulations/turtlebot3_simulations/scriptsCopied!
Create a Python script turtlemovegoal.pyand make executable (chmod +x turtlemovegoal.py).
touch turtlemovegoal.pyCopied!
Be sure to be in the correct directory where the program is located. Make Executable
chmod +x turtlemovegoal.pyCopied!
WARNING
If chmod +x is not execute onto the python script it won't run!
If you execute the command ls in the terminal
you will see that the name turtlemovegoal.pyshould be green.
That indicates that it is executable.
lsCopied!
Add the code below to the python script. Open it with nano editor
nano turtlemovegoal.pyCopied!
TIP
Paste it with CTRL + SHIFT + V in nano editor
With CTRL + S you can save the file and with CTRL + X you can close the file.
python code `move to goal`
#!/usr/bin/env python #!/usr/bin/env python import rospy from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist from turtlesim.msg import Pose from math import pow, atan2, sqrt class TurtleBot: def __init__(self): # Creates a node with name 'turtlebot_controller' and make sure it is a # unique node (using anonymous=True). rospy.init_node('turtlebot_controller', anonymous=True) # Publisher which will publish to the topic '/turtle1/cmd_vel'. self.velocity_publisher = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=10) # A subscriber to the topic '/turtle1/pose'. self.update_pose is called # when a message of type Pose is received. self.pose_subscriber = rospy.Subscriber('/turtle1/pose', Pose, self.update_pose) self.pose = Pose() self.rate = rospy.Rate(10) def update_pose(self, data): """Callback function which is called when a new message of type Pose is received by the subscriber.""" self.pose = data self.pose.x = round(self.pose.x, 4) self.pose.y = round(self.pose.y, 4) def euclidean_distance(self, goal_pose): """Euclidean distance between current pose and the goal.""" return sqrt(pow((goal_pose.x - self.pose.x), 2) + pow((goal_pose.y - self.pose.y), 2)) def linear_vel(self, goal_pose, constant=1.5): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return constant * self.euclidean_distance(goal_pose) def steering_angle(self, goal_pose): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return atan2(goal_pose.y - self.pose.y, goal_pose.x - self.pose.x) def angular_vel(self, goal_pose, constant=6): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return constant * (self.steering_angle(goal_pose) - self.pose.theta) def move2goal(self): """Moves the turtle to the goal.""" goal_pose = Pose() # Get the input from the user. goal_pose.x = float(input("Set your x goal: ")) goal_pose.y = float(input("Set your y goal: ")) # Please, insert a number slightly greater than 0 (e.g. 0.01). distance_tolerance = input("Set your tolerance: ") vel_msg = Twist() while self.euclidean_distance(goal_pose) >= distance_tolerance: # Porportional controller. # https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportional_control # Linear velocity in the x-axis. vel_msg.linear.x = self.linear_vel(goal_pose) vel_msg.linear.y = 0 vel_msg.linear.z = 0 # Angular velocity in the z-axis. vel_msg.angular.x = 0 vel_msg.angular.y = 0 vel_msg.angular.z = self.angular_vel(goal_pose) # Publishing our vel_msg self.velocity_publisher.publish(vel_msg) # Publish at the desired rate. self.rate.sleep() # Stopping our robot after the movement is over. vel_msg.linear.x = 0 vel_msg.angular.z = 0 self.velocity_publisher.publish(vel_msg) # If we press control + C, the node will stop. rospy.spin() if __name__ == '__main__': try: x = TurtleBot() x.move2goal() except rospy.ROSInterruptException: passCopied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
Get file from Github (opens new window)
Source wiki (Moving to goal (opens new window))
# Multiple goals
In the last example we want to navigate to 5 different points. You can use the same setup as the previous examples.
Make a new python script turlepath.pyadd paste the code below.
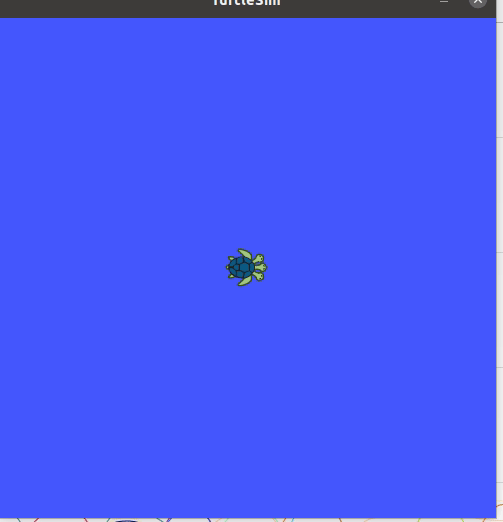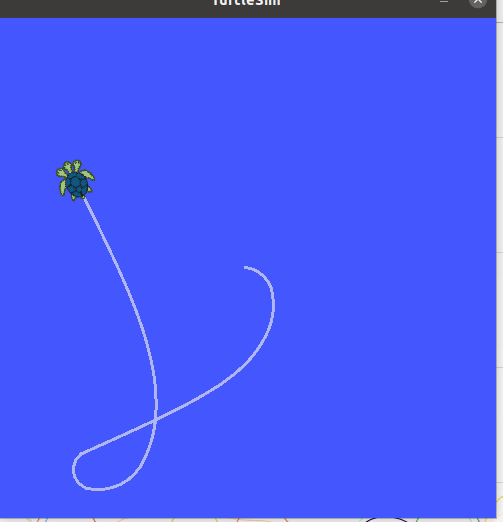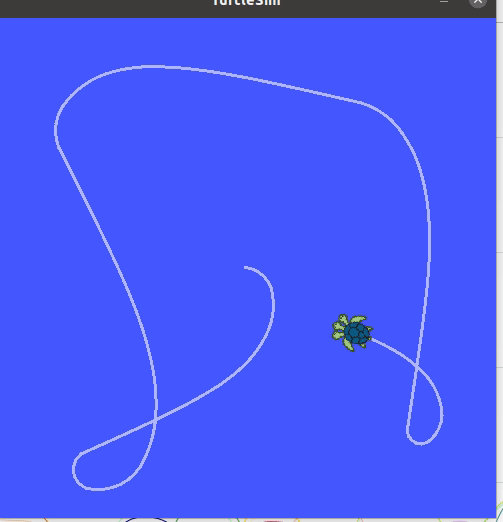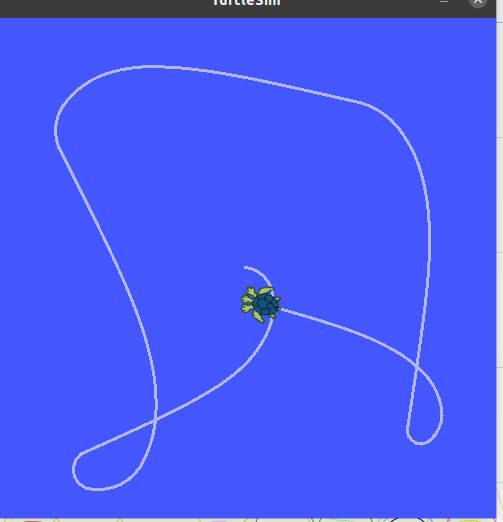
python code `Multiple goals`
#!/usr/bin/env python #!/usr/bin/env python import rospy from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist from turtlesim.msg import Pose from math import pow, atan2, sqrt class TurtleBot: def __init__(self): # Creates a node with name 'turtlebot_controller' and make sure it is a # unique node (using anonymous=True). rospy.init_node('turtlebot_controller', anonymous=True) # Publisher which will publish to the topic '/turtle1/cmd_vel'. self.velocity_publisher = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=10) # A subscriber to the topic '/turtle1/pose'. self.update_pose is called # when a message of type Pose is received. self.pose_subscriber = rospy.Subscriber('/turtle1/pose', Pose, self.update_pose) self.pose = Pose() self.rate = rospy.Rate(10) self.path = [] self.posepoint1 = Pose() self.posepoint1.x = 1 self.posepoint1.y = 1 self.posepoint1.theta= 0 self.path.append(self.posepoint1) self.posepoint2 = Pose() self.posepoint2.x = 1 self.posepoint2.y = 9 self.posepoint2.theta= 0.50 self.path.append(self.posepoint2) self.posepoint3 = Pose() self.posepoint3.x = 9 self.posepoint3.y = 9 self.posepoint3.theta= 1.57 self.path.append(self.posepoint3) self.posepoint4 = Pose() self.posepoint4.x = 9 self.posepoint4.y = 1 self.posepoint4.theta= 0 self.path.append(self.posepoint4) self.posepoint5 = Pose() self.posepoint5.x = 5 self.posepoint5.y = 5 self.posepoint5.theta= 0 self.path.append(self.posepoint5) def update_pose(self, data): """Callback function which is called when a new message of type Pose is received by the subscriber.""" self.pose = data self.pose.x = round(self.pose.x, 4) self.pose.y = round(self.pose.y, 4) def euclidean_distance(self, goal_pose): """Euclidean distance between current pose and the goal.""" return sqrt(pow((goal_pose.x - self.pose.x), 2) + pow((goal_pose.y - self.pose.y), 2)) def linear_vel(self, goal_pose, constant=1.5): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return constant * self.euclidean_distance(goal_pose) def steering_angle(self, goal_pose): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return atan2(goal_pose.y - self.pose.y, goal_pose.x - self.pose.x) def angular_vel(self, goal_pose, constant=6): """See video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qh15Nol5htM.""" return constant * (self.steering_angle(goal_pose) - self.pose.theta) def takepath(self): print(self.path) for point in self.path: print(point) self.move2goal(point) # If we press control + C, the node will stop. rospy.spin() def move2goal(self,point): """Moves the turtle to the goal.""" goal_pose = Pose() # Get the input from the user. goal_pose.x = point.x goal_pose.y = point.y # Please, insert a number slightly greater than 0 (e.g. 0.01). distance_tolerance = 1 vel_msg = Twist() try: while self.euclidean_distance(goal_pose) >= distance_tolerance: # Porportional controller. # https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proportional_control # Linear velocity in the x-axis. vel_msg.linear.x = self.linear_vel(goal_pose) vel_msg.linear.y = 0 vel_msg.linear.z = 0 # Angular velocity in the z-axis. vel_msg.angular.x = 0 vel_msg.angular.y = 0 vel_msg.angular.z = self.angular_vel(goal_pose) # Publishing our vel_msg self.velocity_publisher.publish(vel_msg) # Publish at the desired rate. self.rate.sleep() except KeyboardInterrupt: print("stopped") # Stopping our robot after the movement is over. vel_msg.linear.x = 0 vel_msg.angular.z = 0 self.velocity_publisher.publish(vel_msg) if __name__ == '__main__': try: x = TurtleBot() x.takepath() except rospy.ROSInterruptException: passCopied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
Get file from Github (opens new window)
Interested in other examples python & turtlesim see the following link.
Hopefully you learnt something from this tutorial. 😃
More info visit www.rosdriven.dev